60% of attacks Android aim to steal money
According to the report’s findings “mobile cyber threats,” prepared by Kaspersky Lab and the Interpol between August 2013 and July 2014, 60% of recorded attacks by security products from Kaspersky Lab had intended to steal money from users of Android devices.
Cybercriminals directed their attacks, mostly users against Russia, while Ukraine, Spain, the UK, Vietnam, Malaysia, Germany, India and France also appear on the list of the countries attacked.

In absolute terms, more than 588,000 Android users worldwide suffered attacks with financial malware (Trojan-Trojan-SMS and Banking) during the period analyzed. This figure is six times greater than occurred in the same period last year
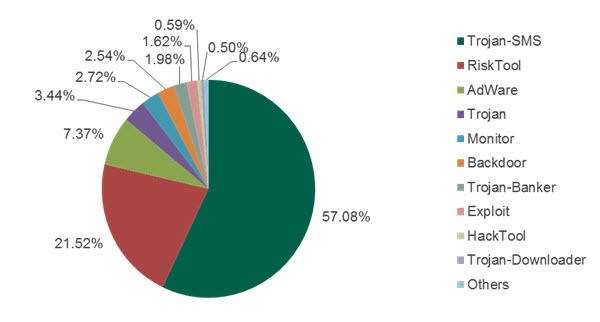
In total, 57.08% of all reported incidents were linked programs for family of malware Trojans, SMS, designed to send short messages to special numbers without charging the users’ knowledge. Russia is the country that receives most of these attacks, with 64.42% of all detections in user devices made by this country antivirus Kaspersky Lab
About a quarter of the attacks Trojan-SMS has been detected in Kazakhstan (5.71%), Ukraine (3.32%), Spain (3.19%), the UK (3.02%), Vietnam (2.41%), Malaysia ( 2.3%), Germany (2%), India (1.55%) and France (1.32%).
Other 1.98% of malware attacks use a Banking Trojan-which, combined with the functionality of the Trojan-SMS is able to steal data from bank cards as well as user names and passwords for online banking services. Russia is at the top of this table, with 90.58% of all-Banking Trojan detections to be registered in the Russian Federation. The remaining top 10 has a relatively low level of attacks and includes Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Belarus, USA, Lithuania, Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, Germany and Uzbekistan.
New trends in mobile threats
Although during the period analyzed the Kaspersky Lab products have registered a relatively small number of attacks on mobile banking Trojans, analysts from security firm indicate that the total number of variants of mobile malware has grown strongly -. the only 423 in August 2013 to 5967 in July 2014 samples, ie, 14 times more
The variants or modifications, are a version of a malicious program that undergoes a slight change from the original malware. This small change can make the malware is less detectable by security solutions. The high level of growth of these variants found during this study shows that cybercriminals are creating multiple variations of malware in its attempt to go unnoticed antivirus solutions and infect as many devices as possible. Usually antivirus companies create a new signature in software to defend this kind of tactic.
“A successful infection by a Trojan-Banking can provide access to the cybercriminal to all the money from his victim, as a Trojan-SMS needs of infecting dozens or even hundreds of devices to achieve a profit that is worth the work. But not all users use online banking applications. This is why there is a big difference in the number of Trojan and Trojan-SMS-Banking recorded attacks on our products, “explains Roman Unuchek, senior virus analyst at Kaspersky Lab.
” During the recent years have witnessed a considerable increase in the number of mobile cyber threats, which have also grown increasingly complex and intelligent enough to achieve specific entities. With the mobile market growing exponentially, it becomes increasingly clear that these threats are mutating to include new attack vectors that allow them to explore personal devices, “noted Madan Oberoi, Director of ciberinovação and dissemination in INTERPOL Global Complex for Innovation
Via EmpresasHoje
.
-> – border-bottom
Filed in category:
->
No comments:
Post a Comment